John Smith
Oct. 8, 2024, 2:45 a.m.This 2-day tour to Luxor was absolutely fantastic! From the moment we left Sahel Hashesh, every detail was meticulously planned. Visiting temples like Madinet Habu and The Ramseum was an awe-inspiring experience. The Valley of the Queens was a personal highlight. Our guide was knowledgeable and passionate. Highly recommend!
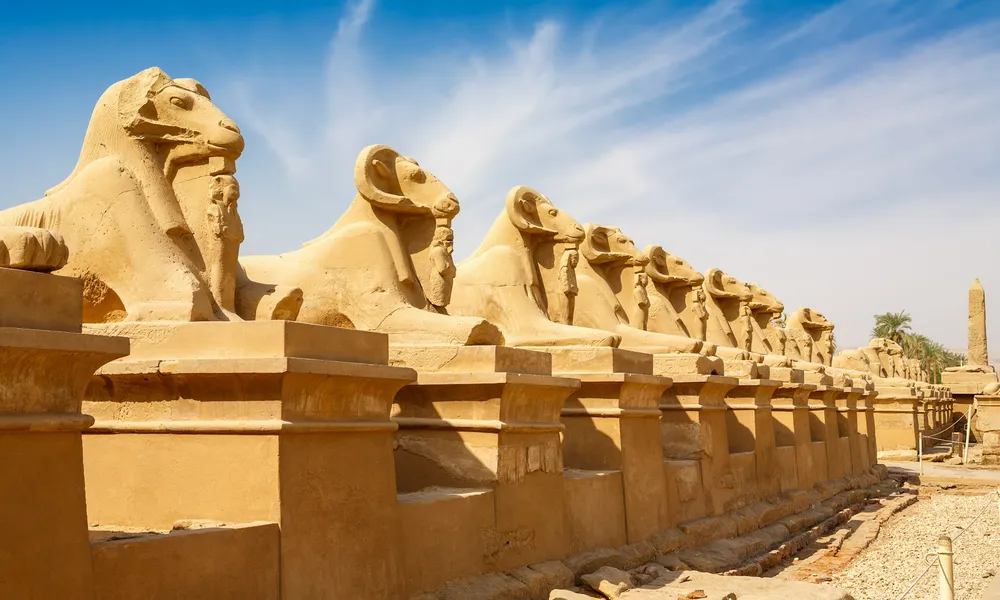
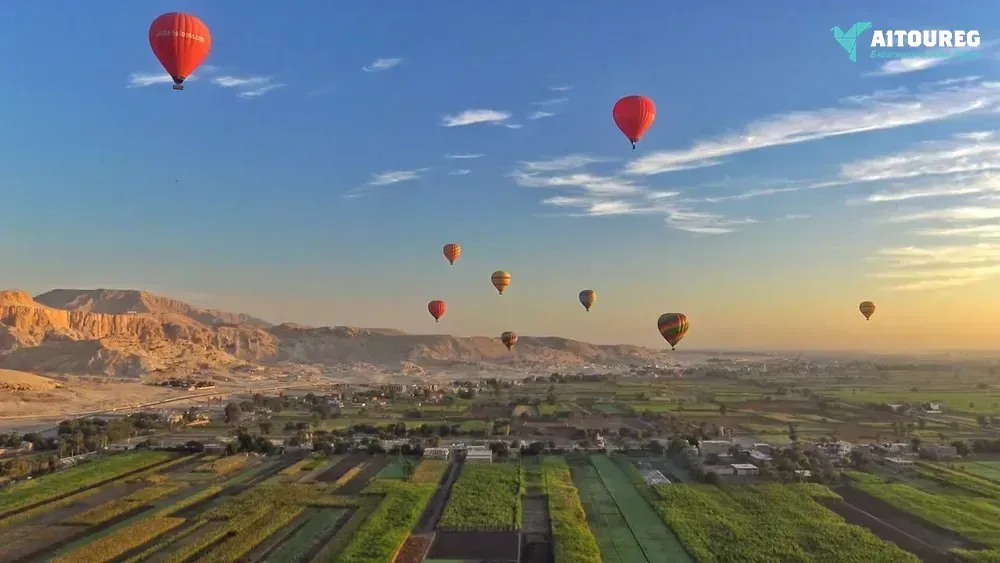
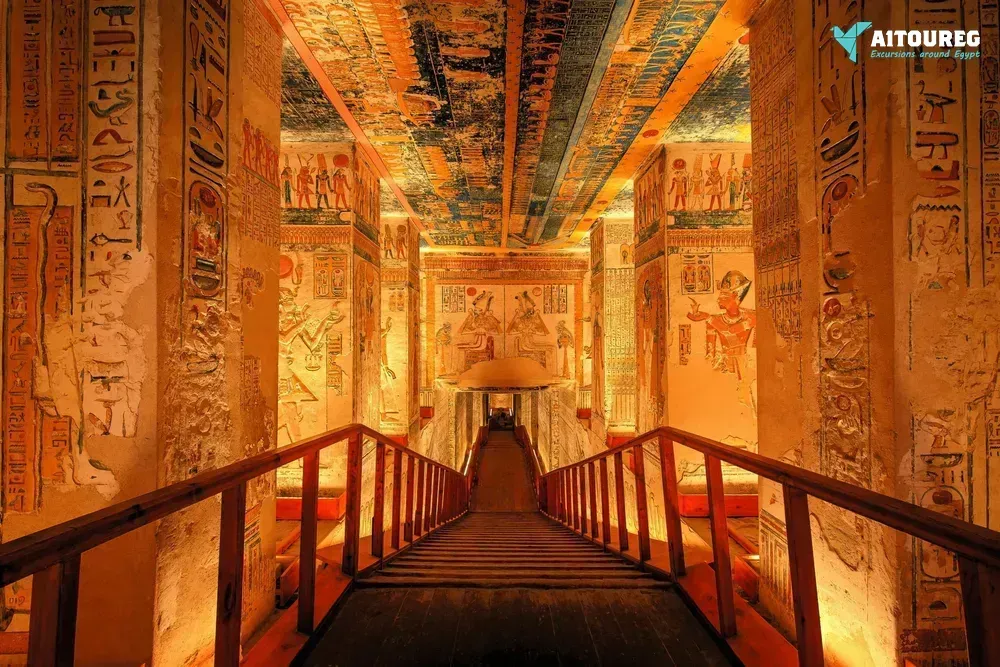
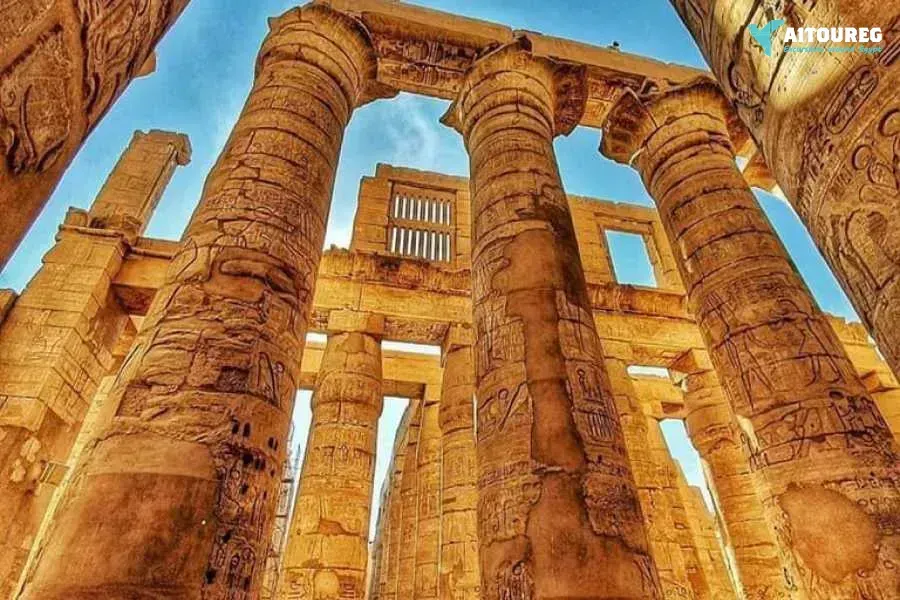
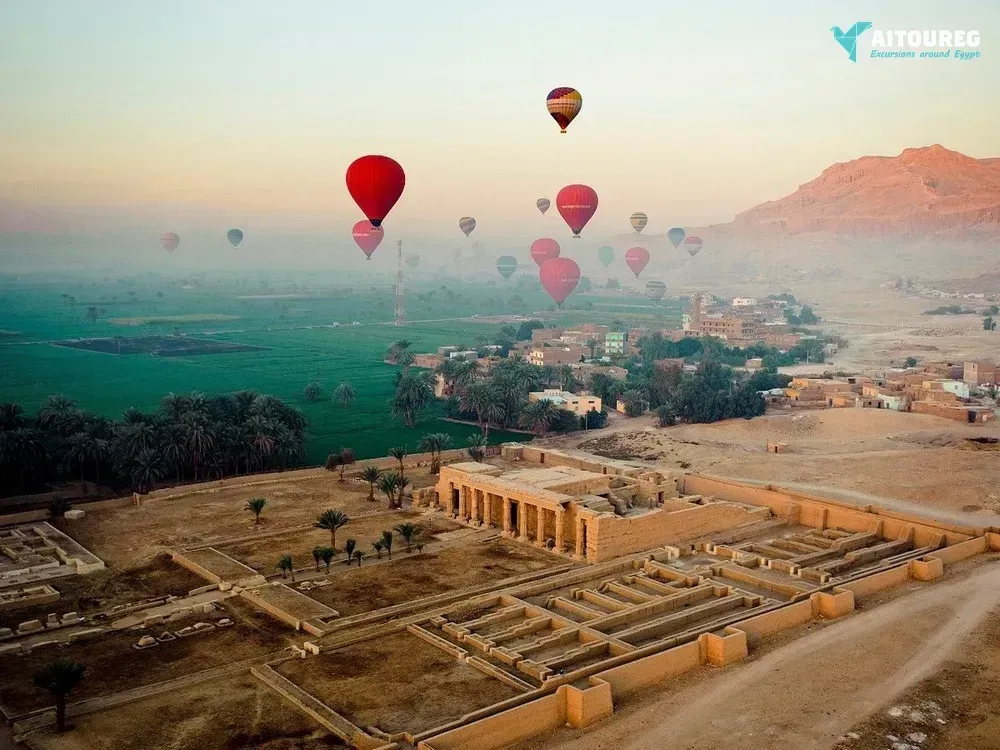
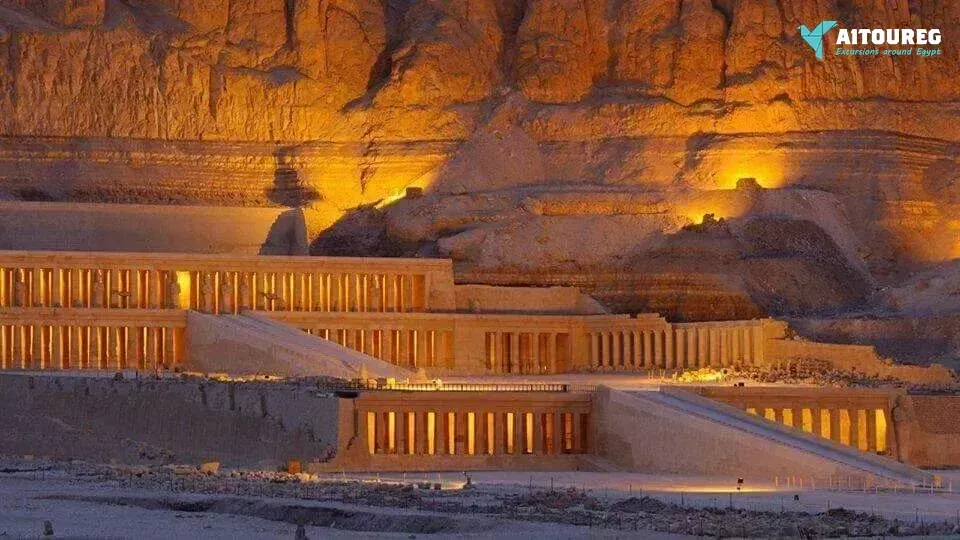
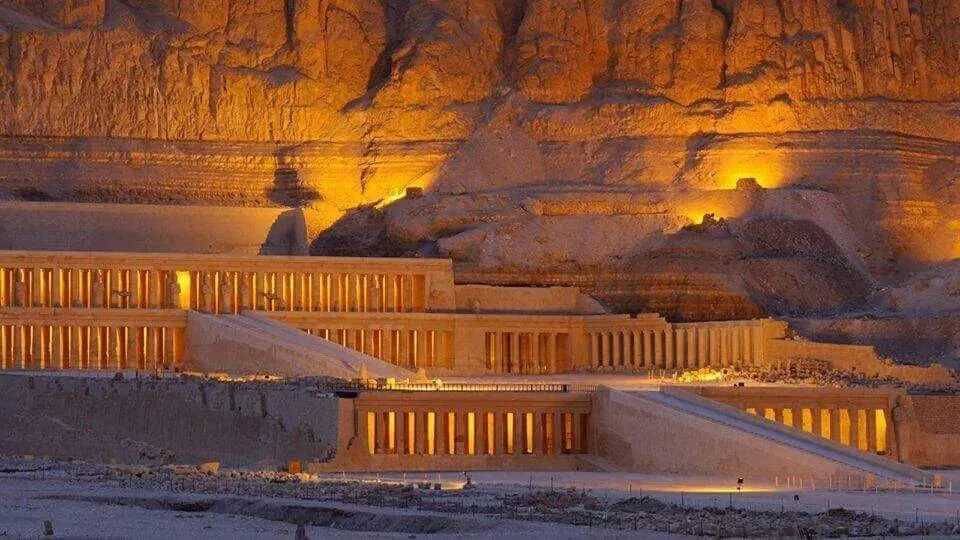
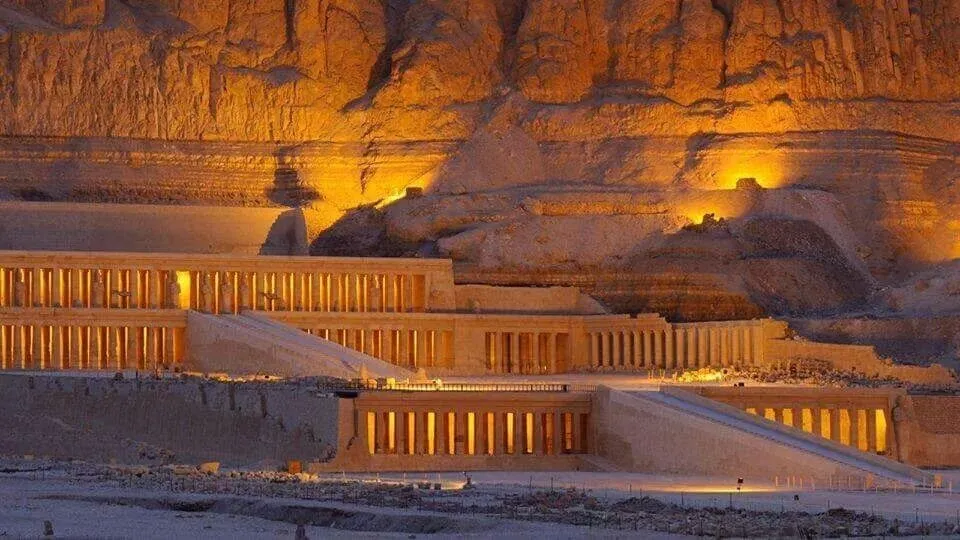
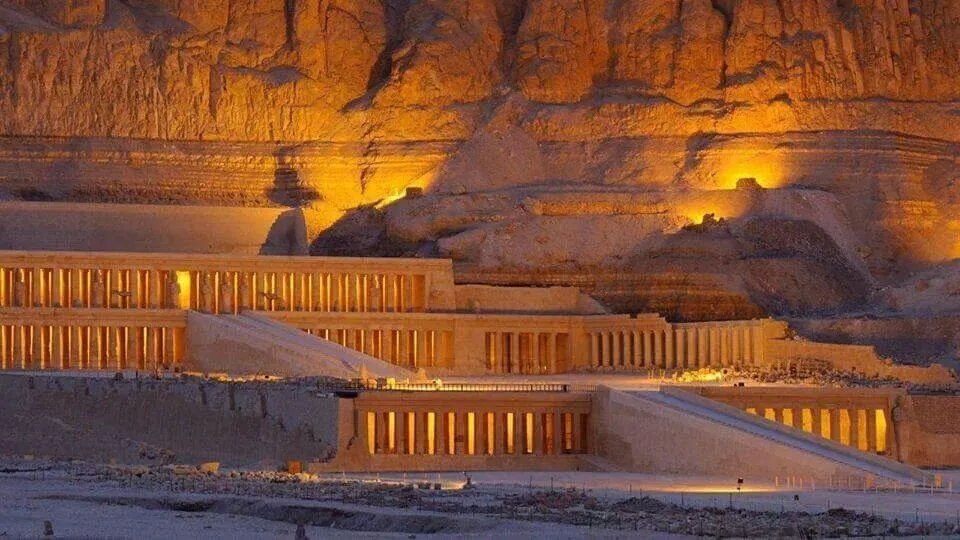



















1) Day 1 Sahel Hashesh- Luxor
Early morning, we will pick you up from your hotel in Sahel Hashesh by a private A.C. Car to be transferred to Luxor for an overnight trip to Luxor from Marsa Alam . Upon arrival you will meet your private tour guide who will join you to visit: Madinat Habu temple : In ancient times Madinat Habu was known as Djanet and according to ancient belief was the place was Amun first appeared. Both Hatshepsut and Tuthmosis III built a temple dedicated to Amun here and Later Rameses III constructed his larger memorial temple on the site. First Pylon – the temple of Rameses III During his time Djanet became the administrative center of Western Thebes. The whole temple complex was surrounded by a massive fortified enclosure wall, with an unusual gateway at the eastern entrance, known as the pavilion gate. This structure, a copy of Syrian migdol fortresses is something you would not expect to see in Egypt. Rameses III, a military man probably saw the virtue in such a structure. It is likely Rameses resided here from time to time because a royal palace was attached at the south of the open forecourt of this temple, while priests’ dwellings and administrative buildings lay on either side of the temple. Originally a canal with a harbor outside the entrance connected the temple to the Nile. But this was obliterated by the desert long ago. Madinat Habu temple from the air Ramsseum: Ramesseum, funerary temple of Ramses II (1279–13 BC), erected on the west bank of the Nile River at Thebes in Upper Egypt. The temple, famous for its 57-foot (17-meter) seated statue of Ramses II (of which only fragments are left), was dedicated to the god Amon and the deceased king. The walls of the Ramesseum, which is only about half preserved, are decorated with reliefs, including scenes depicting the Battle of Kadesh, the Syrian wars, and the Festival of Min Deir El Madina The main cemetery of the royal workmen at Deir el-Medina is situated to the west of the village, on the slope of the Theban hills. Most of the tombs were built during the 19th dynasty. Some of them are impressive in their decoration and size. By the time of the 20th dynasty, the tombs had been turned into family tombs in which the descendants of the original owners were buried. Little alterations were made apart from the addition of another subterranean burial chamber. The lower courses of the eastern hill of Qurnet Murai were the site of burials of babies and children. More than a hundred children were buried in common domestic pottery jars or amphorae, in baskets, even fish baskets, in chests, boxes or in proper coffins there. The poorest burials were those of still-born babies. They contained no jewelry or amulets, only small vessels filled with food for the afterlife. The adults' graves were situated higher up. Many of these graves date from the 18th dynasty Lunch During the tour. The valley of The Queens The Valley of the Queens, also known as Biban el-Harim, Biban el-Sultanate, and Wadi el-Melikat, is a place in Egypt where wives of Pharaohs were buried in ancient times. In ancient times, it was known as Ta-Set-Neferu, meaning - 'the place of the Children of the Pharaoh', because along with the Queens of the 18th, 19th and 20th dynasties (1550-1070 BCE) many princes and princesses were also buried with various members of the nobility. The tombs of these individuals were maintained by mortuary priests who performed daily rituals and provided offerings and prayers for the deceased nobility. The valley is located near the better known Valley of the Kings on the west bank of the Nile across from Thebes (modern Luxor ) . This barren area in the western hills was chosen due to its relative isolation and proximity to the capital. The kings of the 18th dynasty, instead of the traditional building of pyramids as burial chambers (perhaps because of their vulnerability to tomb robbers), now chose to be buried in rock-cut tombs. This necropolis is said to hold more than seventy tombs, many of which are stylish and lavishly decorated. An example of this is the resting place carved out of the rock for Queen Nefertari (1290-1224 BCE) of the 19th Dynasty. The polychrome reliefs in her tomb are still intact. The ancient Egyptians gave it the name Set Neferu, meaning "seat of beauty". From 1903-1906 an Italian expedition discovered about eighty tombs, some of which belonged to children of royalty. Many were severely damaged having been burned and or reduced to being used as stables for donkeys and camels. One of the most well-known tombs is that of Nefertari, the best-loved of Ramesses II's numerous wives. In her honor, he built a beautiful temple at Abu Simbel. On the Evening you can Enjoy An Optional Tour Sound and Light Show at Karnak : The show starts with a historical introduction covering the birth of the great city of Thebes and the erection of the Karnak
: The show starts with a historical introduction covering the birth of the great city of Thebes and the erection of the Karnak  Temple.
Temple.  temple encloses. Overnight at 5 Hotel.
temple encloses. Overnight at 5 Hotel.
The show narrates the glorious achievements of some great Pharaohs as you listen to a magnificent and poetic description of the artistic treasures and great legacy which the Karnak
2) Day2 Luxor - Sahel Hashesh
Breakfast at your hotel then you will be accompanied by your private tour guide and a private air-conditioned vehicle to visit: Luxor Museum This wonderful museum has a well-chosen and brilliantly displayed and explained collection of antiquities dating from the end of the Old Kingdom right through to the Mamluk period, mostly gathered from the Theban temples and necropolis. The ticket price puts off many, but don't let that stop you: this is one of the most rewarding sights in Luxor and one of the best museums in Egypt. Drive to Dendera temple Dendera temple The Temple of Hathor was largely constructed during the Late Ptolemaic period, specifically during the reign of Ptolemy XII and Cleopatra VII. Later additions were made during the Roman period. Although built by a dynasty of rulers who were not native Egyptians themselves, the design of this temple has been found to be in accordance to that of other classical Egyptian temples, with the exception of the front of the hypostyle hall, which, according to an inscription above the entrance, was constructed by Emperor Tiberius. Apart from these, there are also scenes in the temple complex portraying the Ptolemaic rulers. For example, carved onto the external face of one of the temple walls is a huge relief of Cleopatra VII and her son by Julius Caesar and co-ruler, Ptolemy XV (better known as Caesarion). The two Ptolemaic rulers are shown dressed in Egyptian garb, and offering sacrifices. Hathor was also regarded as a goddess of healing, and this is evident in the presence of a sanatorium in the temple complex. Here, pilgrims would come to be cured by the goddess. Sacred water (which was made holy by having it poured onto statues inscribed with sacred texts) was used for bathing, unguents were dispensed by the priests of Hathor, and sleeping quarters were provided for those hoping that the goddess would appear in their dreams, and so aid them.
Lunch will be served in Qena then we drive you back to your hotel in Sahel Hashesh.